Real GDP: Price x Quantity ; value of output produced in constant based year prices that is adjusted for inflation. Can increase from year to year only if output increases.
Nominal GDP: Price x Quantity ; value of output produced in current year prices. Can increase from year to year if either prices or output increases
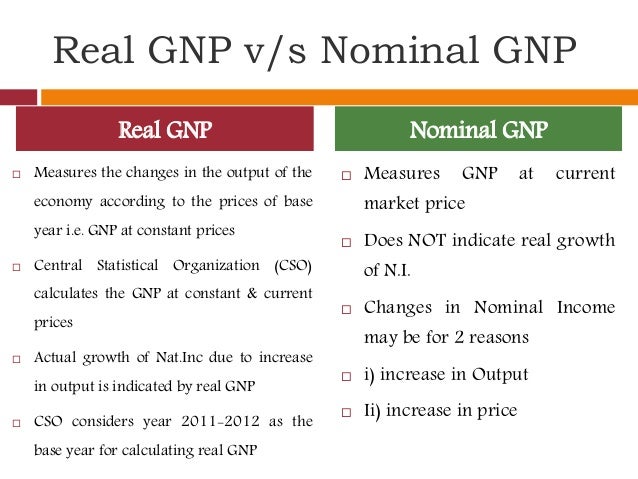
In the base year, current prices is equal to base year (constant) prices
In years after the base year, nominal GDP exceeds real GDP
In years before the base year, real GDP exceeds nominal GDP
GDP Inflator: a price index used to adjust from nominal to real GDP
In the base year, the GDP deflator = 100
For years after the base year, GDP Deflator > 100
For years before the base year, GDP Deflator < 100
Deflator Formula: new-old/old
GDP Deflator = (nominal GDP/real GDP x 100)
Inflation: a general rise in the price level (new[price index]-old[price index] /old x 100) will result in percentage
Consumer Price Index: measures cost of market basket of goods for a typical urban American family (cost of market basket of goods in a given year / cost of market basket of goods in the base year x 100)
Inflation: reduces purchasing power of money. When inflation occurs, each dollar of income will buy fewer goods than before.
3 causes of inflation:
- government prints too much money,
- governments that keep printing money to pay debts end up with the situation called hyperinflation,
- demand-pull inflation: too many dollars chasing too few goods and demands pulls up prices // cost-push inflation: higher production cost increases prices
Unanticipated Inflation:
- Hurt: Lenders (borrow at a fixed rate), fixed income (social security, retired; COLA adjustment), Savers (money in bank)
- Help: Borrowers, debtors, flexible income (fluctuates over time),
- Business where price of product increases faster than price of resources
Nominal Interest Rate: unadjusted cost of borrowing or lending out money
Real Interest Rate: cost of borrowing or lending money that is adjusted for inflation (nominal interest rate - inflation)
In the base year, Nominal GDP is equal to Real GDP.
ReplyDelete