Balance of Payments: Measure of Money inflows and outflows between US and rest if world; inflows referred as “credits” and outflows referred as “debits”
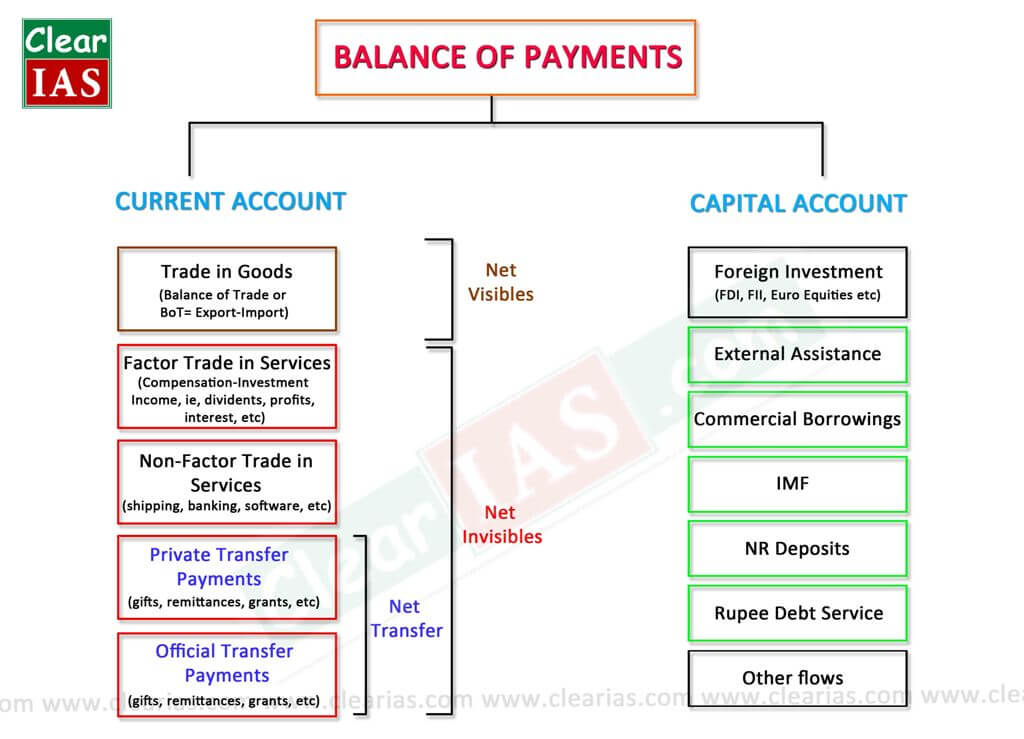
Balance of Payment divided into 3 accounts:
- Current Account: Balance of Trade aka Net Exports, Net Foreign Income aka Net Investment: income earned by US owned by foreign assets, Net Transfers: foreign aid
- Capital/Financial Account: Includes purchase above real and financial access (ex: direct investment- in US, debit is credit to capital account; brand factory in area); direct investment by US firms/individuals in a foreign country are debits to capital account; purchase of foreign financial asset reps a debit to capital account (ex: rich buys stock in petral China); purchase of domestic product reps purchase of credit in financial account (ex: Venezuela buys steak from Venezuela); current and capital account should zero each other out; Real asset: real estate, G & Financial asset: stocks or bonds
- Official Reserves: foreign currency holdings of US federal reserve bank
every transaction in Balance of Payments is recorded twice
Equations:
*Balance of Trades = Goods Exports + Goods Imports
*Balance of Goods & Services = Goods Exports + Services Exports - Goods Imports + Services Imports
*Balance on Current Account = Net Exports + Net Investments + Net Transfers
*Capital Account = Foreign Purchases on Assets + US Purchases of Foreign Assets
Foreign Exchange: buying and selling of currency; difference between appreciation and depreciation
Appreciation: increase of value of a country’s currency with respect to a foreign country’s currency; dollar said to be stronger, less units of dollars needed to buy single unit of other currency
Depreciation: loss of value of country’s currency with respect to foreign currency; dollar said to be weaker, more units of dollar is needed to buy single unit of other currency
Absolute Advantage: producer can produce most output or requires least amount of inputs
Comparative Advantage: producer with lowest opportunity cost
Input: It takes a certain amount of input to get a certain product (ex: apples to make a pie)
Output: certain amount of product out of given input (ex: mph, $1/gum)
Comments
Post a Comment